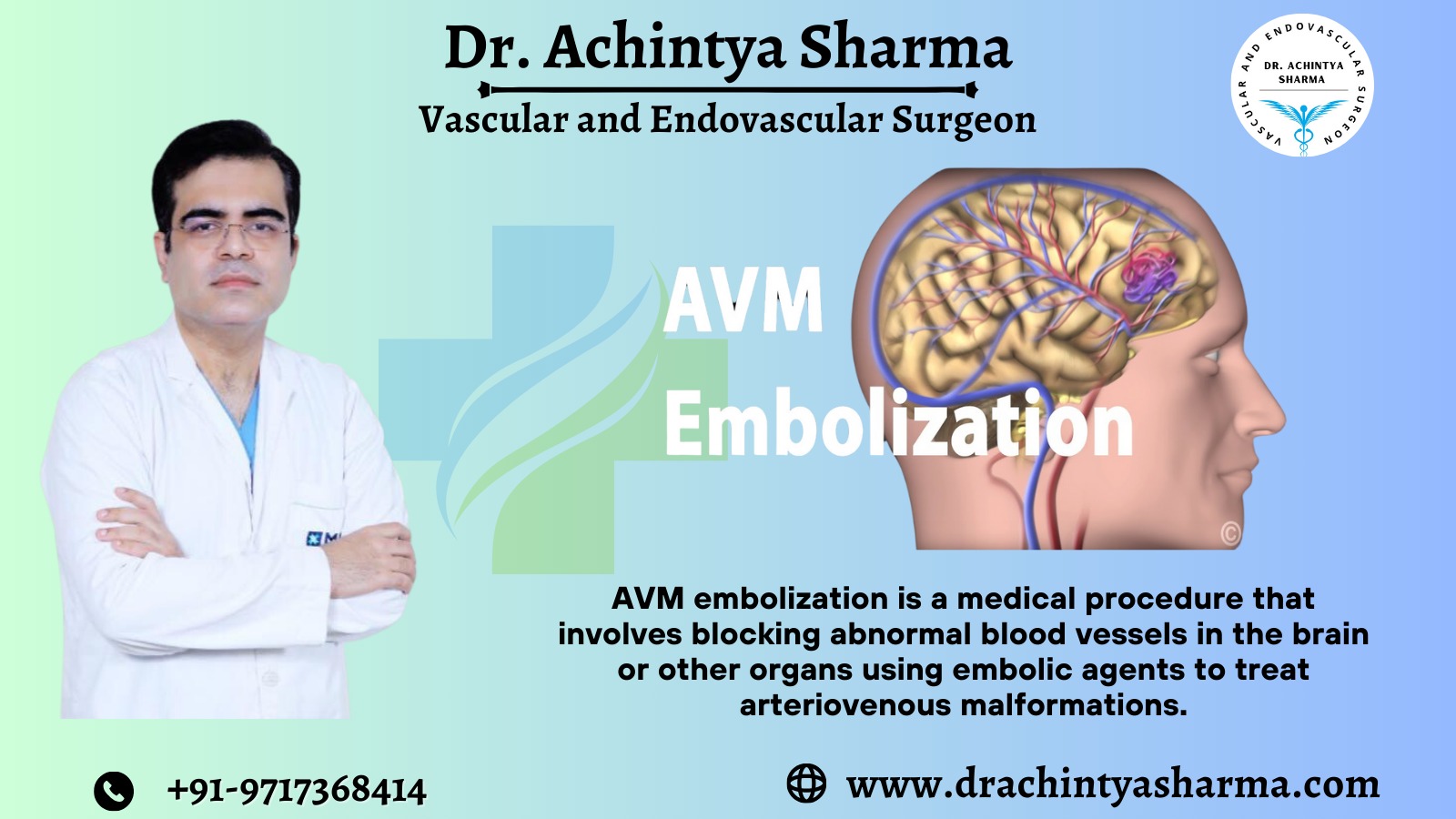
Arteriovenous malformations are abnormal tangles of blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, which disrupt normal blood flow. AVMs can occur anywhere in the body, but when located in the brain, they pose a significant health risk are In the case of cerebral AVMs, the risks are particularly high due to the delicate nature of brain tissue. Irregular blood flow causes an AVM to rupture, leading to serious consequences such as bleeding and neurological deficits. Advances in medical innovation are shaping the healthcare landscape, fostering innovation, and providing effective solutions. AVM embolization has emerged as a groundbreaking procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of these anomalies. Fortunately, advances in medical science provide a ray of hope through a procedure called embolization.
The Basics Explanation of AVM Embolization:
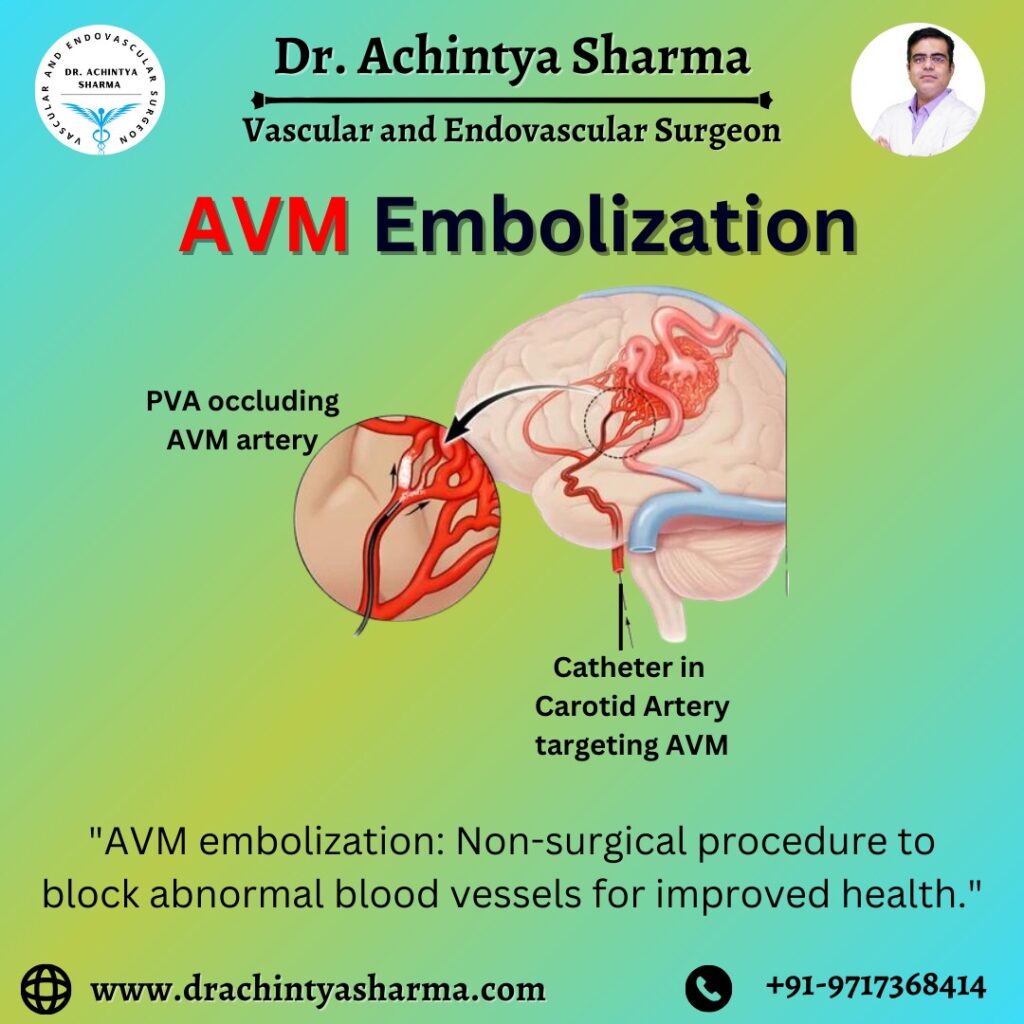
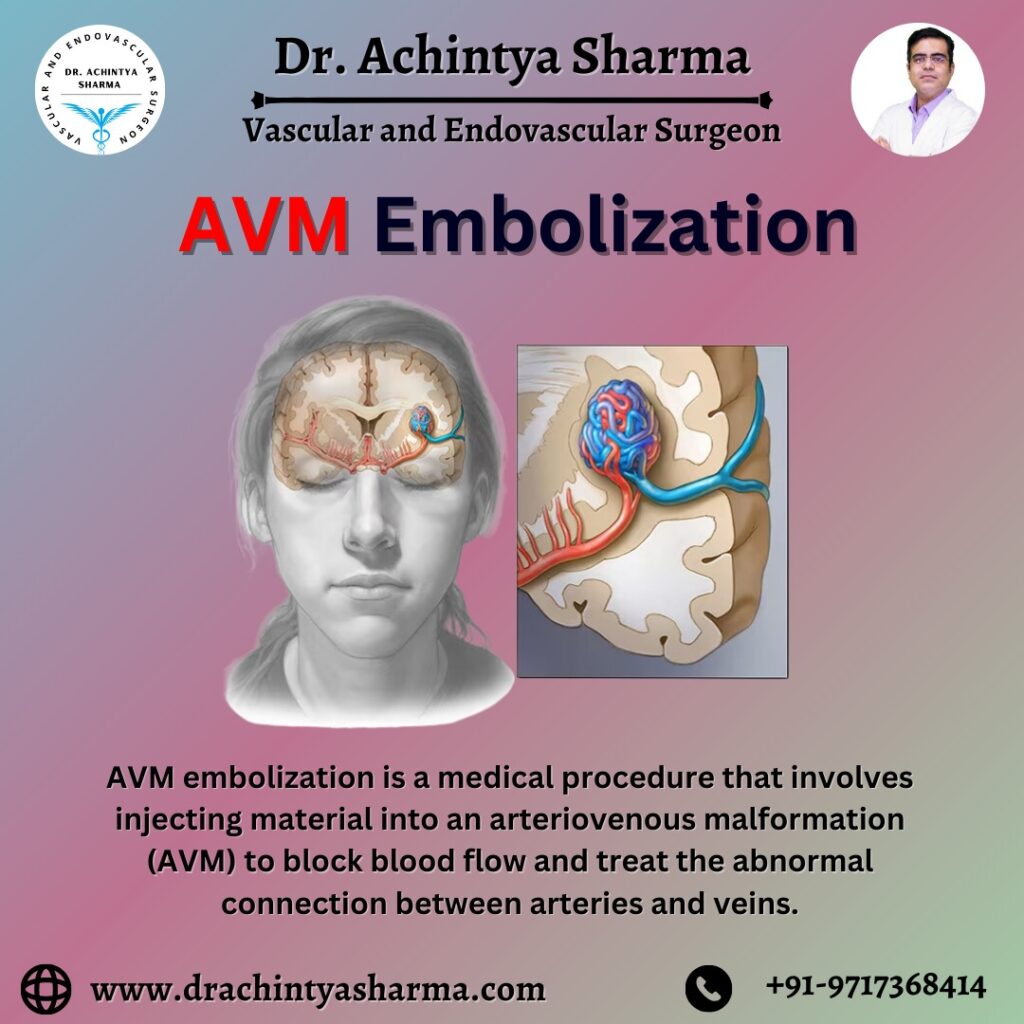
Arteriovenous malformation embolization is a minimally invasive procedure, designed to treat AVMs by blocking abnormal blood vessels. This is achieved by injecting special glue-like substances or small particles into the vessels, causing them to clot and effectively closing the abnormal connection. The goal is to redirect blood flow and prevent the risk of bleeding, which can have serious and potentially life-threatening consequences.
Benefits of AVM Procedure:
1. Minimally Invasive:
This invasive procedure is performed through catheterization, reducing the need for open surgery. This minimally invasive approach shortens recovery time and reduces the risks associated with major surgical procedures.
2. Reduced risk of bleeding:
Arteriovenous malformation Embolization Procedure significantly reduces the risk of bleeding associated with AVMs. By closing the abnormal vessels, the procedure helps prevent potential ruptures that could lead to hemorrhagic stroke.
3. Protection of brain function:
It is important to protect the delicate brain tissue. This invasive procedure aims to preserve brain function by eliminating abnormal blood flow without the need for more invasive surgical procedures.
4. Improved quality of life:
Successfully treating AVMs through arteriovenous malformation embolization can improve a patient’s quality of life. Relief from symptoms such as headaches and seizures can significantly improve daily life.
5. Precise Targeting:
The interventional radiologist can precisely navigate the catheter to the site of the AVM, ensuring targeted treatment while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
6. Reduced Risk of Rupture:
By blocking abnormal blood flow within the AVM, embolization significantly reduces the risk of rupture, thereby reducing potentially devastating consequences such as bleeding.
Challenges and future directions:
While Embolization has shown remarkable success, challenges such as the risk of recurrence and long-term outcomes still need to be carefully considered. It may only be suitable for some patients or some AVM cases. The decision to pursue this procedure is made individually, taking into account factors such as the location and size of the AVM, the overall health of the patient, and the associated risks. Ongoing research aims to refine embolic materials, enhance imaging technologies, and optimize the overall process for better outcomes.
Conclusion:
AVM embolization stands as a testament to the continued evolution of medical technology in addressing complex healthcare issues. As medical science advances, these procedures provide a path to treatment. Which marks a transformative era in the management of vascular abnormalities. As advances in interventional radiology continue, embolization promises to refine its efficacy further and expand its application to benefit increasing numbers of patients worldwide. This not only addresses the immediate risks but also seeks to improve the long-term well-being of individuals affected by this complex condition.