The carotid artery is one of the most important blood vessels in the human body, responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the brain, neck, and face. Located on either side of the neck, these arteries play a crucial role in ensuring the brain receives the nutrients it needs to function effectively. Any disruption in the flow of blood through the carotid arteries can have serious consequences, including an increased risk of stroke.
In this blog, we address common questions about the carotid artery, including its function, associated health conditions, and ways to maintain its health. By understanding more about these essential arteries, you can take proactive steps to protect your brain and overall well-being.
What are Carotid Arteries?
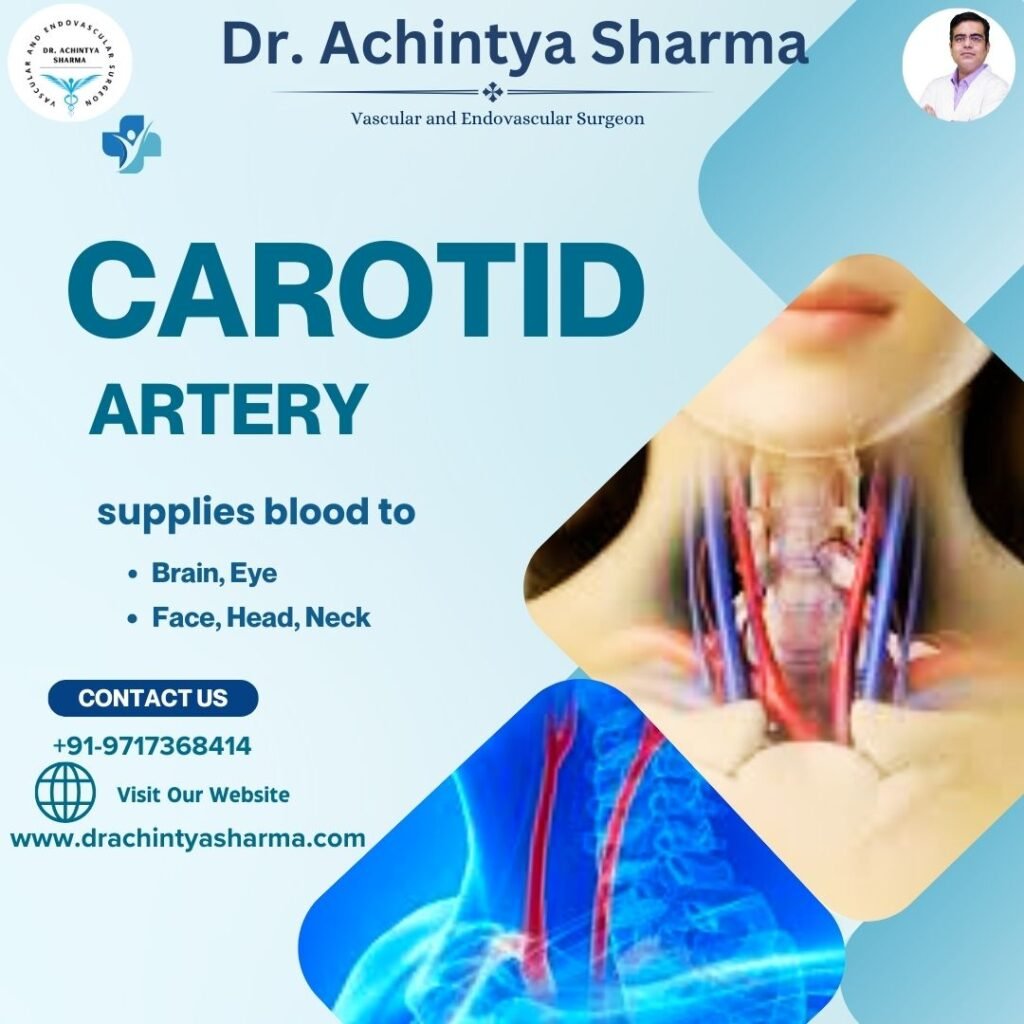
The carotid arteries are two broad arteries that put in the neck on both the bilateral sides.They are part of the circulatory system, which carries blood to the heart and other parts of the body.Each carotid artery branches into two parts:
Internal Carotid Artery:
This provides blood supply to the brain, eyes and certain regions of face.
External Carotid Artery:
This proceeds to furnish blood to the face, head, and neck.
What Makes Carotid Arteries Special?
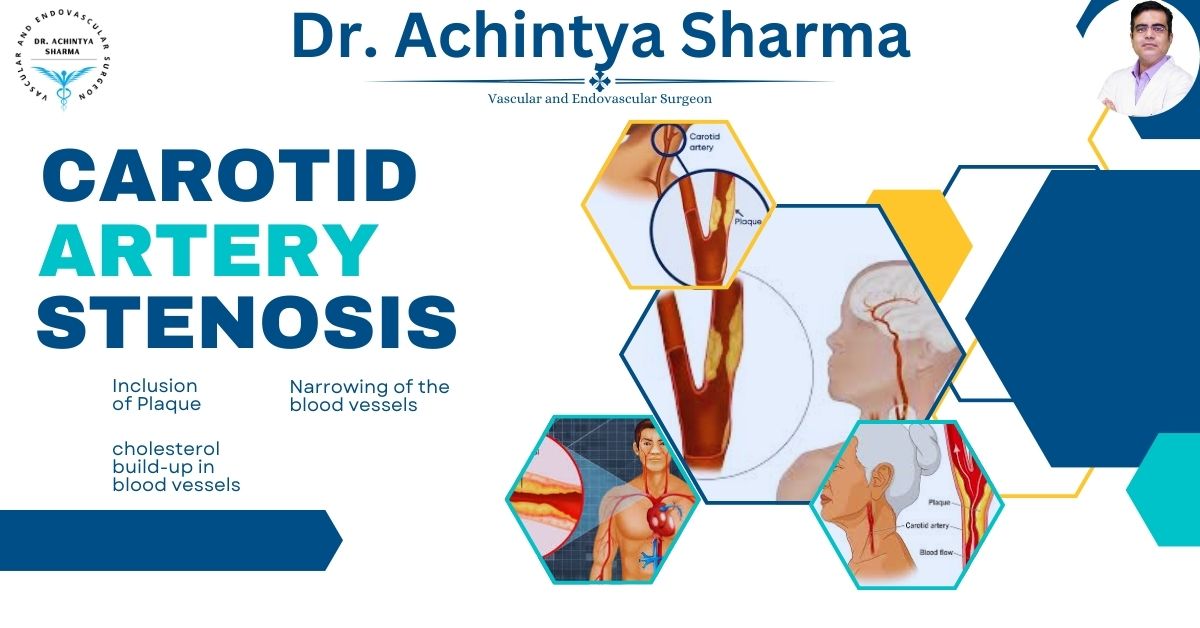
The brain is essentially the control center of the body and is also one of the greatest consumers of energy, using approximately 20 percent of the oxygen one inhales. Moreover, since the carotid arteries convey the major blood flow to the brain, they are absolutely vital for any motor, sensory, or cognitive functions. However, these arteries can become blocked or damaged. As a result, this can lead to serious health issues, such as a stroke.
Potential Issues of the Carotid Arteries
Carotid arteries can have problems and most of them are related to the lifestyle or the aging process. Some of the common problems include:
1. Carotid Artery Disease
Deposits of fatty materials called plaques on the inner walls of the carotid arteries characterize carotid artery disease. This condition is also referred to as atherosclerosis Slowly, the plaques are hard and can cause the arteries to become narrow leaving less blood supply to the brain. If the plaque buildup worsens or the plaque ruptures, clots form and completely block blood flow.
2. Stroke
A stroke occurs when something cuts off blood flow to a part of the brain This may result from the blockage of blood flow to the brain in the carotid artery (Ischemic stroke) or rupture of a damaged artery (Haemorrhagic stroke). One of the most considerable threat factors relating to ischemic strokes is carotid artery disease.
3. Carotid Artery Aneurysm
Here, part of the wall of carotid artery becomes thinned and protrudes outwards, and it is a comparatively rare ailment. An untreated aneurysm will burst and this may lead to serious complications to the life of the patient.
What are the symptoms of carotid artery problems?
The problems of carotid arteries often appear asymptomatic. However, something might warn, especially if the blood circulation to the head is limited tightly.
These include:
A person who has a sudden loss of strength or feeling on one half of the body, in the face, arm or leg.
Problems with speaking or understanding to others who are speaking.
Temporary loss of vision in one eye.
Dizziness or loss of balance.
How It Is Diagnosed: Carotid Artery Problems
Doctors use various methods to assess the health of the carotid arteries:
Ultrasound:
It is a painless procedure that uses sound waves to create images of the internal organs of the body.
CT or MRI Angiography:
These imaging tests give better pictures of the blood vessels.
Physical Examination:
A doctor may listen with a stethoscope for the abnormal sound in the neck known as bruits, which indicates that blood is flowing through some specific zone in a turbulent way.
How to Avoid Carotid Artery Disease
Taking care of your carotid arteries is very important for avoiding such severe problems as strokes. Here are some practical tips:
Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet:
Make sure your meal contains lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grain products and low fat proteins. Avoid saturated fats and salt and sugar intake.
Exercise Regularly:
Engaging in physical activity enhances circulation making your arteries more flexible and healthy. Ideally it is suggested that an individual should exercise for at least thirty minutes in a week.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking affects blood vessels, and speeds up the formation of plaques that can accumulate in arteries. Quitting can help potentially decrease your likelihood of developing the condition or CAD, CAA’s precursor.
Regular Check-Ups:
The condition usually doesn’t show any symptoms at first, but regular check ups will advise when you have to seek a doctor for investigation regarding your carotid arteries.
Treatment Options:
If carotid artery disease is diagnosed, treatment options depend on the seriousness of the condition:
Lifestyle Changes and Medication:
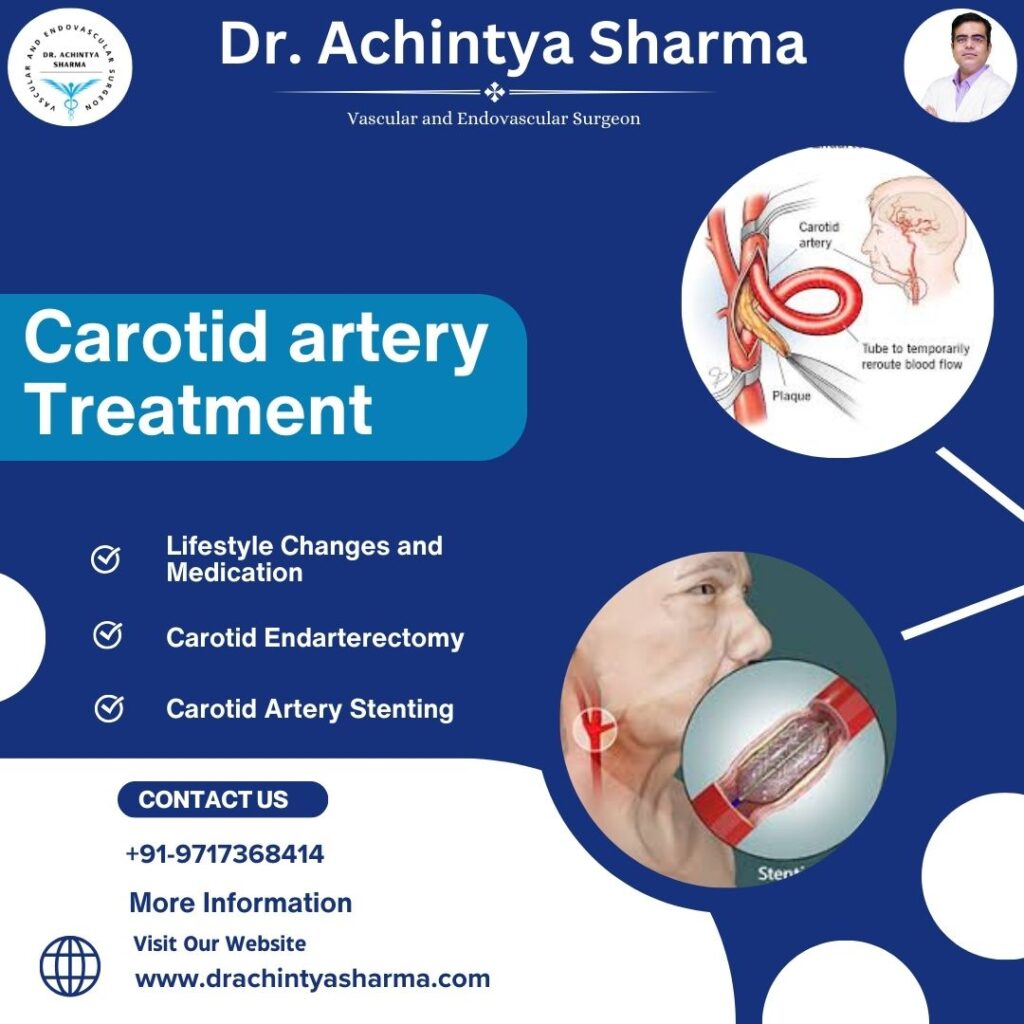
People with mild cases can lead normal lives and take drugs such as cholerific acid reducing drugs and other blood thinning drugs.
Carotid Endarterectomy:
This surgery involves cleaning of plaques from the artery to allow free blood flow.
Carotid Artery Stenting:
In this non-surgical procedure, doctors place a narrow, cylinder-like device (stent) on the walls of the artery.
Conclusion
The carotid arteries are crucial roads through which your brain must be supplied with blood that will enable its cells to survive. Maintaining the health of these arteries should be a concern for all humans. With better dietary plans, regular exercising and health checkups you can shield yourself against critical conditions such as strokes and lead a better life.