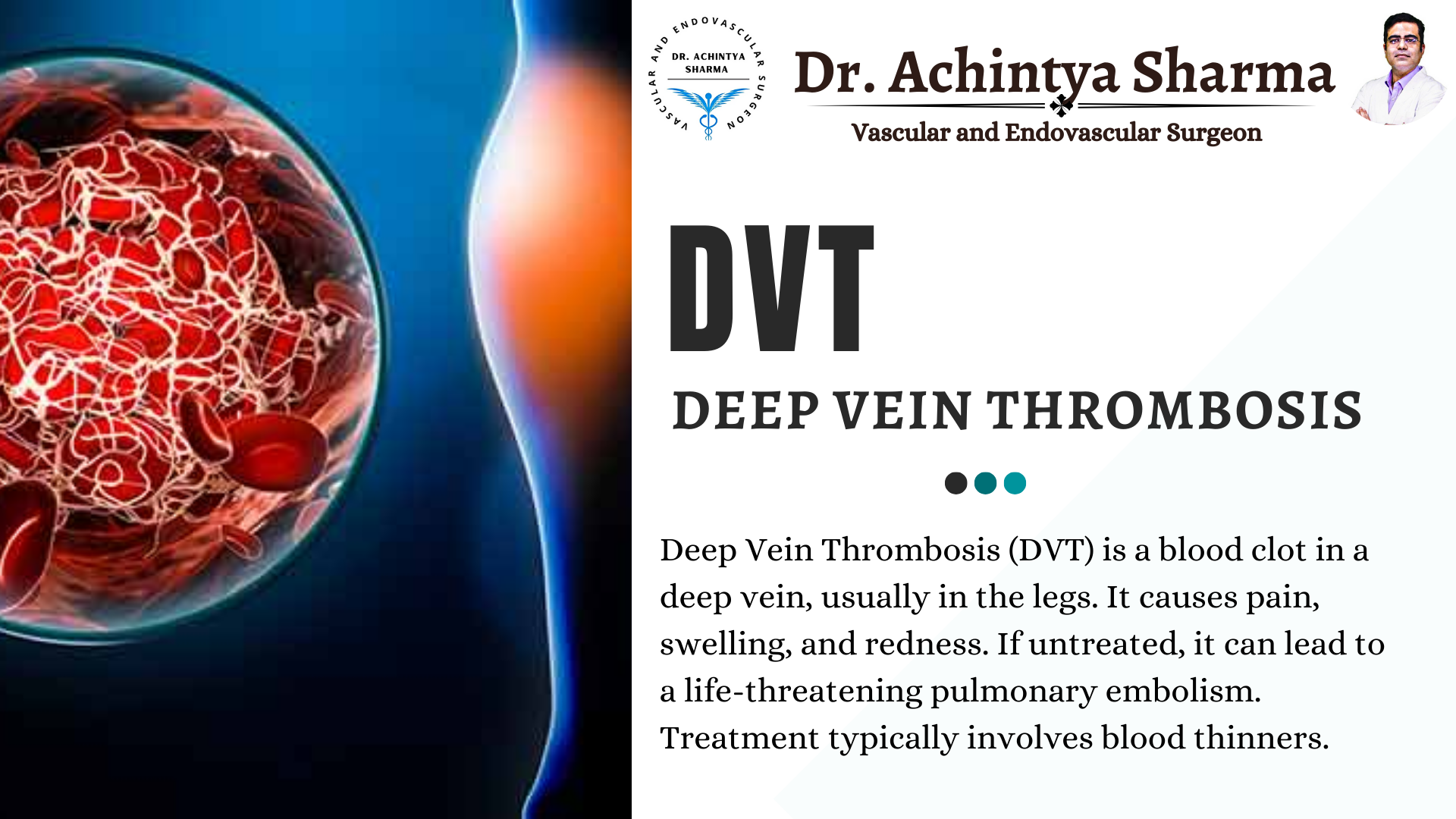
Deep thrombosis, often referred to as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), is a critical condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, commonly in the legs. If not properly managed, deep thrombosis can lead to severe complications, such as pulmonary embolism, where the clot travels to the lungs. Effective deep thrombosis treatment is essential for preventing these outcomes and ensuring patient safety. This blog will provide a detailed overview of various deep thrombosis treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and more advanced procedures.
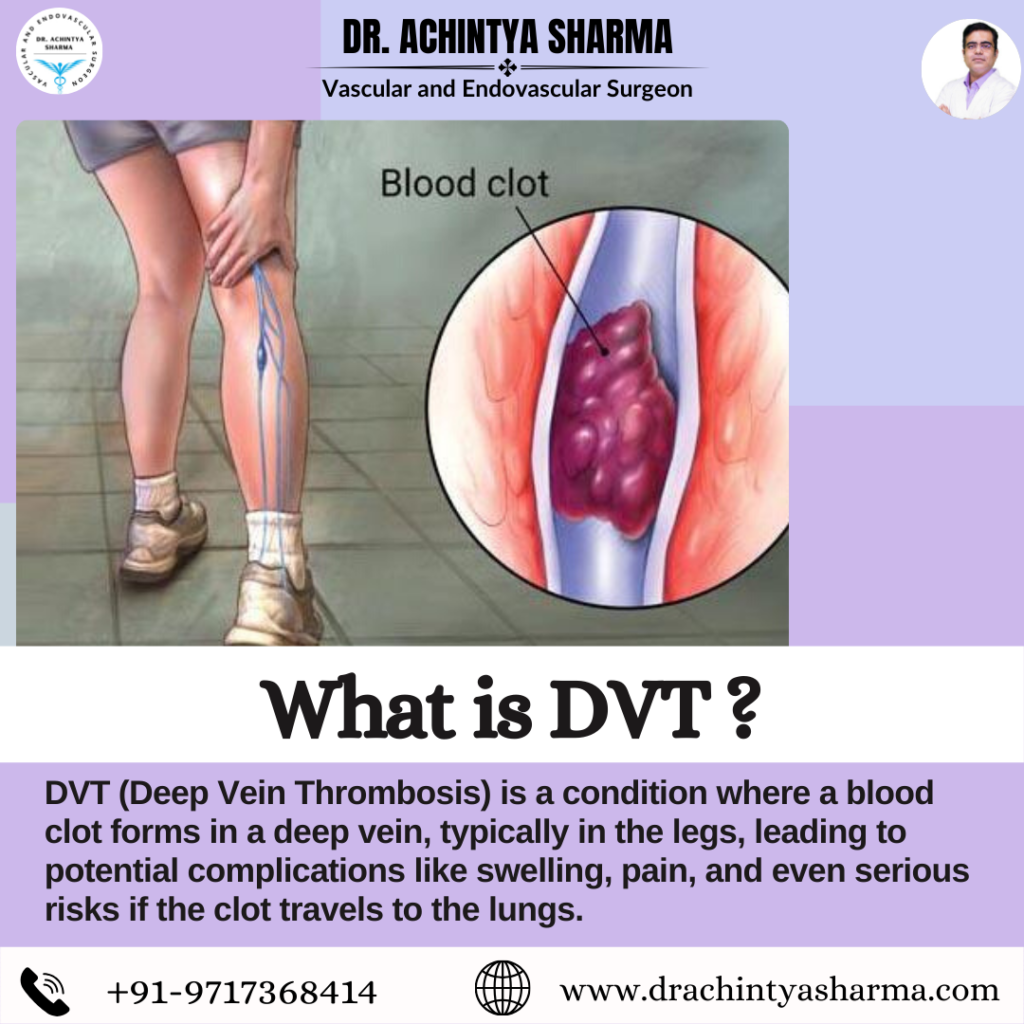
Understanding Deep Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when blood clots form in deep veins, usually in the legs. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgeries, and certain medical conditions. Recognizing symptoms like swelling, pain, and skin discoloration is crucial for timely and effective treatment.
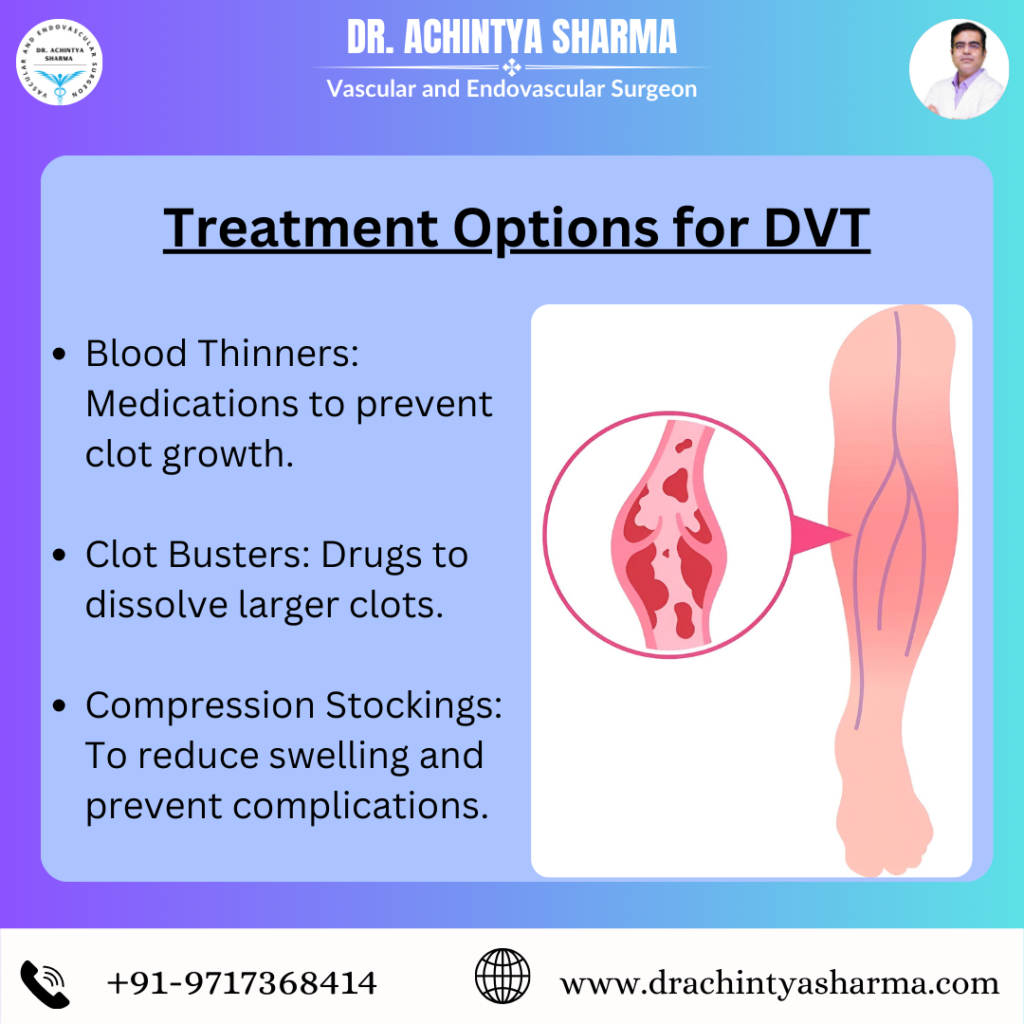
Treatment Options for Deep Thrombosis
Effective treatment for deep thrombosis involves a combination of medical therapies, lifestyle modifications, and occasionally, surgical interventions. Here are the key strategies for managing deep thrombosis:
- Anticoagulant Medications :
Anticoagulants are the primary treatment for deep thrombosis. These medications help prevent the clot from enlarging and reduce the likelihood of new clots forming. The main types include:
- Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): Medications such as rivaroxaban, apixaban, and edoxaban fall into this category. They are popular choices due to their ease of use and lack of need for regular monitoring in deep thrombosis treatment.
- Vitamin K Antagonists: Warfarin is a traditional anticoagulant that requires frequent blood tests to monitor its effectiveness. Despite the need for regular testing, it remains a reliable option for deep thrombosis treatment.
- Thrombolytic Therapy
In more severe cases of deep vein thrombosis, doctors may require thrombolytic therapy. This treatment involves administering medications that rapidly dissolve blood clots. Medical professionals typically use thrombolytics in acute situations where quickly resolving the clot is necessary to prevent further complications.
- Mechanical Interventions
Doctors consider mechanical treatments for deep vein thrombosis when other methods are inadequate. These treatments include:
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in the management of deep thrombosis. Incorporating these adjustments can significantly impact overall deep thrombosis treatment success:

- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity helps improve circulation and reduce the risk of clot formation associated with deep thrombosis.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains supports vascular health and can aid in the management of deep thrombosis.
- Avoiding Prolonged Immobilization: To prevent deep thrombosis, avoiding long periods of inactivity, such as during long flights or bed rest, is essential. Simple leg exercises can enhance circulation and reduce clot risk.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are vital components of deep thrombosis treatment. Regular check-ups ensure that the treatment plan remains effective and allows for adjustments as needed. Patients should remain alert for any signs of complications and communicate openly with their healthcare team.
Conclusion
Effective deep thrombosis treatment encompasses a range of strategies, from anticoagulant medications and thrombolytic therapy to lifestyle changes and mechanical interventions. By combining these approaches, patients can manage their condition more effectively and reduce the risk of severe complications such as pulmonary embolism. Consulting with healthcare professionals to tailor the treatment plan to individual needs is essential for optimal outcomes in deep thrombosis treatment. With a proactive approach and appropriate medical care, managing deep thrombosis can lead to a better quality of life and improved health.