DVT is a condition in which a blood clot develops within deep veins, most commonly in the legs. Some of the signs it can produce include oedema, pain, erythema, and tumour in the region of the limb. DVT often presents with few or no symptoms, making it difficult sometimes to diagnose. It is crucial to not overlook DVT because if the blood clot comes loose and travels to the lung, that is dangerous and leads to what we call pulmonary embolism. Risk factors include inactivity for long periods, surgery, some health ailments, and smoking. Early identification of the normalized signs and getting a doctor is important to deal with complications and provide right care.
Understanding DVT Symptoms
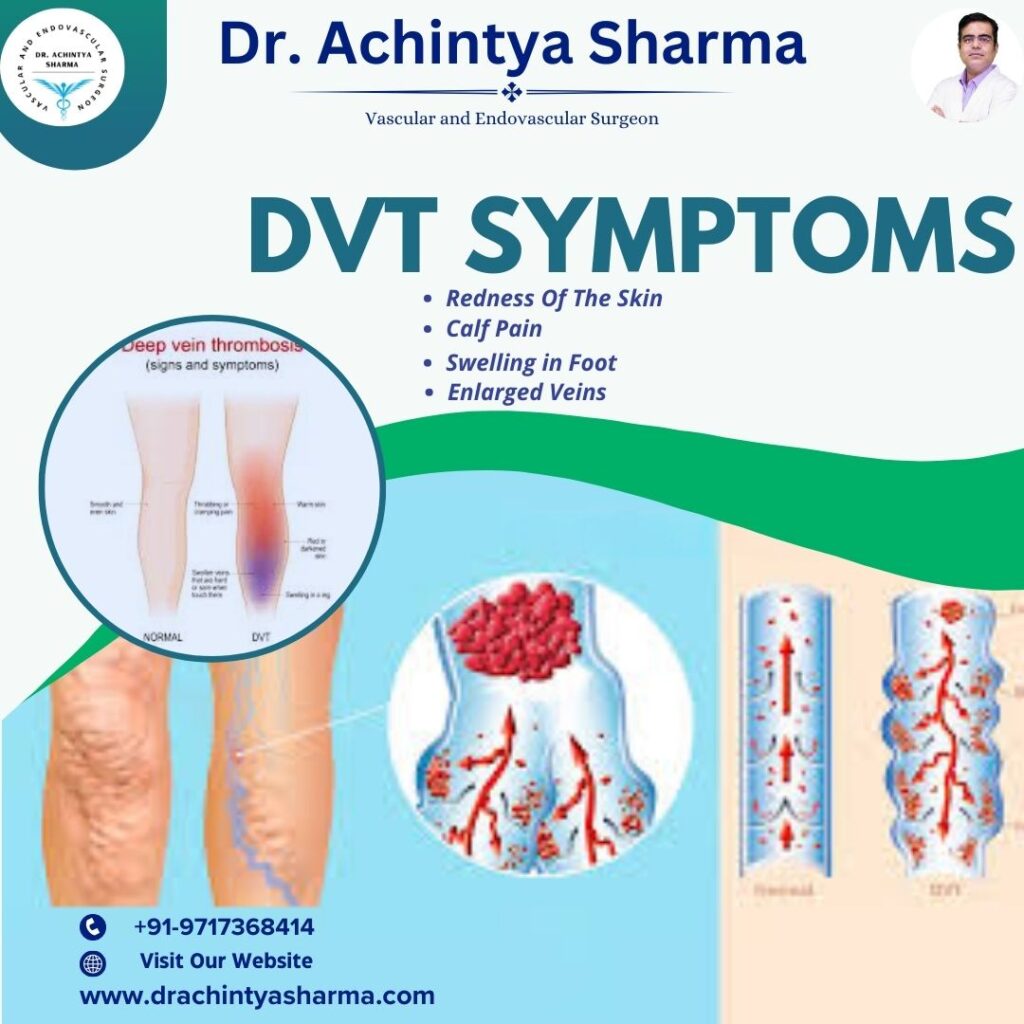
Common Warning Signs
Leg Swelling
One of the major signs is enlargement particularly in the leg. It happens because of the hindrance to the circulation of blood in veins owing to clotting. Knowing this is one of the DVT symptoms is important because erroneously dismissing it may be disastrous.
Pain or Tenderness
Another feature of DVT symptoms is pain in the calf or thigh that persists and grows worse when an individual is strolling or standing.
Skin Discoloration
Skin discoloration is another DVT symptom; red or blue skin around the affected area owing to poor circulation.
Warmth in the Affected Area
The skin over the clot may be warm to touch due to an inflammation of the vein caused by the blockage. A feeling of warmth in the affected limb is another DVT symptom.
Rare Symptoms
Visible Vein Changes
Them is a perception of bigger veins that look inflated as well as signal DVT indicators.
Unexplained Fatigue
Another less recognized DVT symptom is just general fatigue resulting from the poor circulation of blood in the vein.
Risk Factors for DVT
Prolonged Immobility
Lack of mobility during travel or when in bed, for example, by sitting or lying down for extended hours also raises the chances of coming down with DVT symptoms.
Surgery or Injury
Any recent surgery, particularly orthopedic ones, increases the risk of getting DVT.
Menstrual cycle and Hormonal treatment
Hormonal changes during pregnancy directly affect pelvic veins, and the growing fetus increases pressure, making women more vulnerable to DVT.
Chronic Conditions
Cancer, heart diseases, obesity, or other conditions all put a person several notches closer to experiencing the DVT symptom.
Why Early Detection Matters
Recognizing DVT symptoms early can prevent severe outcomes, such as:
Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A condition that is fatal when a clot goes to the lungs.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome: The late consequences, such as pain and inflammation, are usually a result of uncontrolled initial signs of DVT.
Diagnosis of DVT
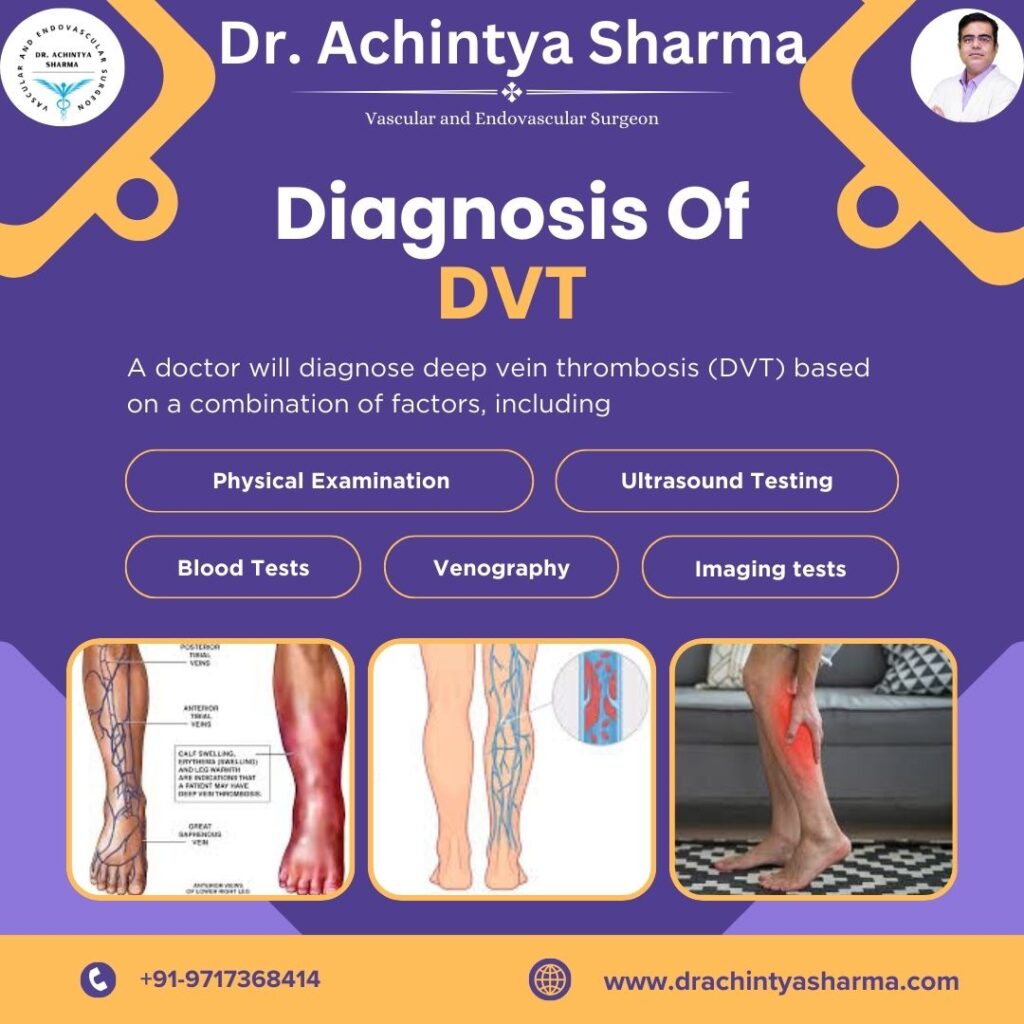
Physical Examination
The initial things that doctors look for are signs of pain, observed over the affected area, enlargement, and color changes which are features of DVT.
Ultrasound Testing
This procedure is non-invasive and provides for the detection of clots in the veins satisfactorily. It is often employed if signs of DVT appear.
Blood Tests (D-dimer):
This protein is generally increased during clotting; therefore, increased levels may affirm the existence of the DVT symptom.
Venography:
Where dye is injected to characterise vein problem with focus made on patients who continue to express signs of DVT after reception of treatment.
Preventing DVT
Stay Active
Keep moving your legs while traveling or working to reduce the risk of blood clots and DVT symptoms
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Staying physically active, getting regular exercise, and practicing stress reduction prohibit the formation of DVT.
Medical Consultation
Those who fall in the high risk category should consult their doctors on whether they should take preventive medicines or steps that can deal with DVT.
Treatments for DVT Symptoms
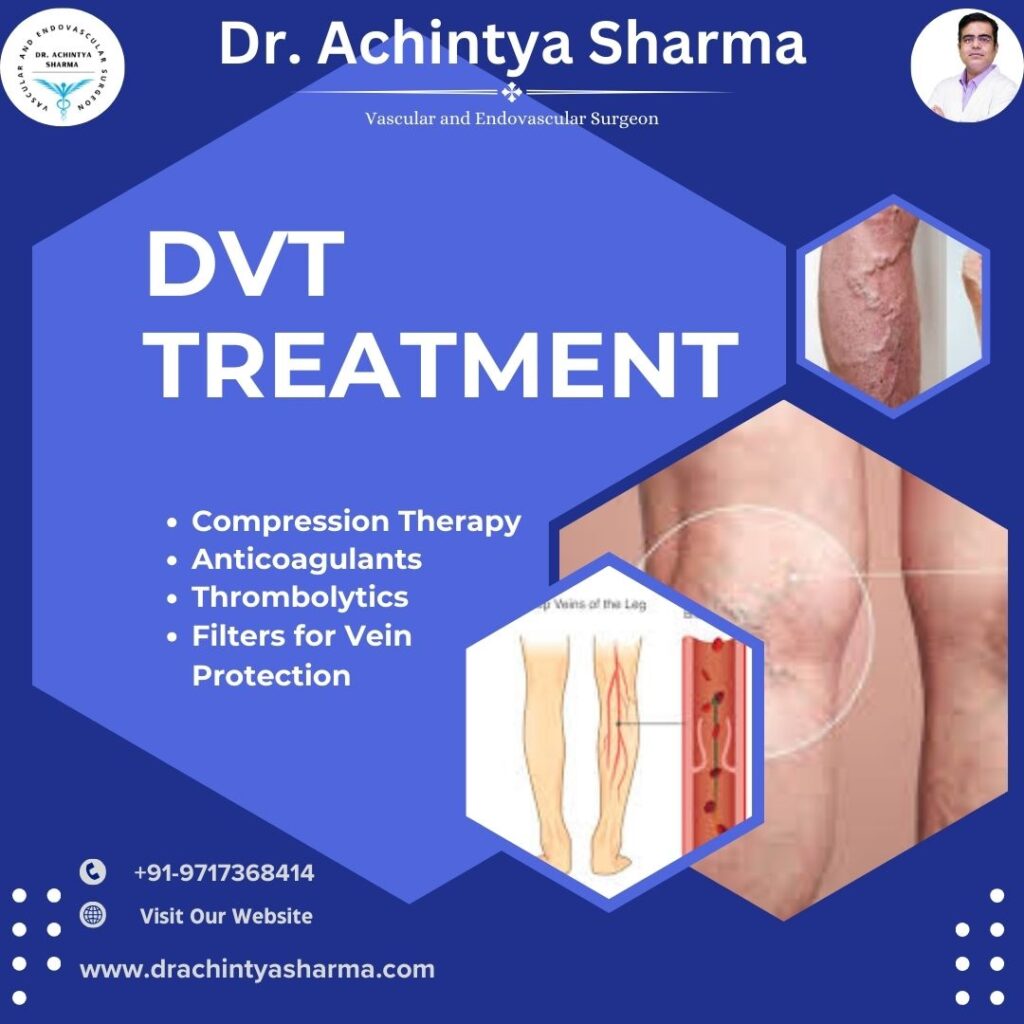
Blood Thinners (Anticoagulants):
These drugs stop the expansion of existing clots or the formation of new ones, thus relieving DVT symptoms.
Clot-Dissolving Drugs (Thrombolytics):
Applied in situations where a huge clot must be dissolved within a short time to minimize severe DVT signs.
Filters for Vein Protection:
Given through a vein to prevent blood clots from traveling to affected organs, particularly in worsening cases of DVT.
Compression Therapy:
Reduction of pain and puffiness, increased blood flow, and this makes DVT sufferers find relief without much hustle.
Importance of Follow-Up Care
The cases of DVT also require regular surveillance and control of the symptoms despite adequate initial treatment. Regular check-ups ensure:
Proper blood thinning levels.
The analysis also excludes secondary outcomes, such as preventing the recurrence of DVT symptoms.
Sepsis severely complicates infections and requires rapid treatment to avoid serious consequences. Severe complications may also emerge almost simultaneously with the onset of a severe infection.
Living with DVT
Small lifestyle changes can make DVT easier to manage
Drink water and do not sit for a long period of time.
Use the guidelines laid down herein to optimise low impact exercises into daily lives.
Keep an eye out for any of the DVT symptoms that may persist such as swelling or pain.
Conclusion
Early signs and signs of DVT include; swelling of the leg or lower extremities, pain in the affected area, redness, and skin warmth in the area that is affected. Not all may experience symptoms but paying attention to the possible symptoms will help avoid complications such as pulmonary embolism. If you have any of these symptoms especially if you are able to experience any of the risk factors like prolonged inactivity or recently undergone surgery, then it is advised that you consult your healthcare provider instantly. The best outcomes and least dangers can be attained if treatment is started and implemented at an early stage. Truly, awareness and response as early as possible are vital in minimising or preventing the risks associated with DVT as well as improving the overall quality and safety of a person’s health.