Even if you don’t have symptoms of peripheral artery disease, you may need to be screened if you are:
Our Service
PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASES
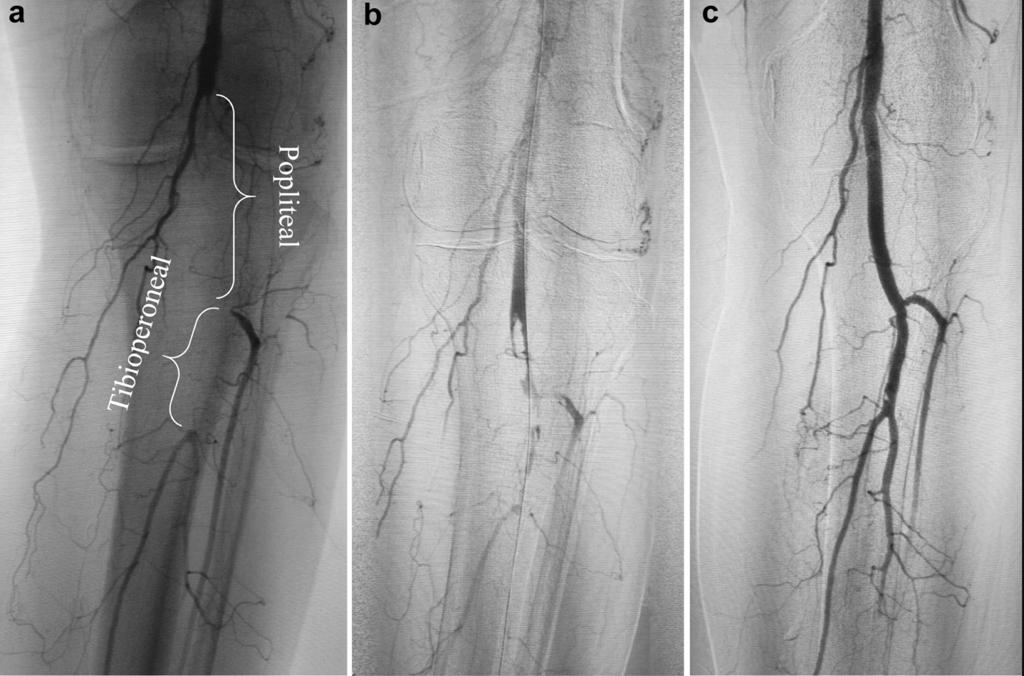
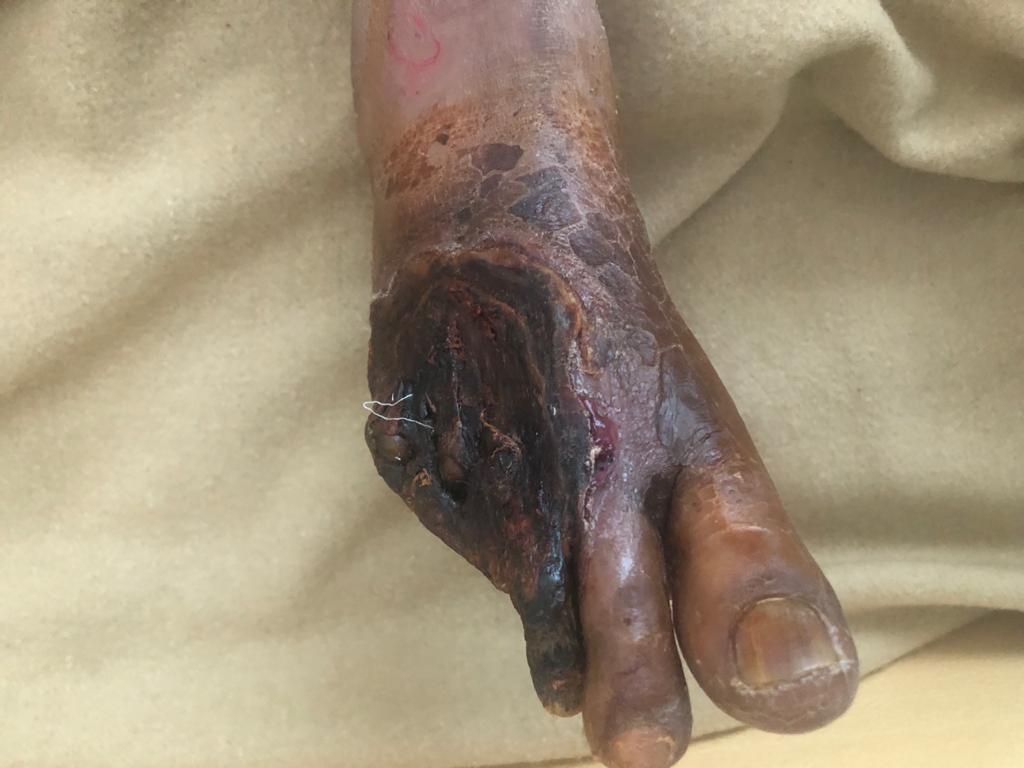
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD] or peripheral arterial disease (PAD] is the blockage of arteries of the lower limbs due to accumulation of cholesterol, calcium and plaques. This leads to reduced blood and oxygen supply to the legs and may eventually lead to limb amputations as well as suffering due to rest pain and gangrene.
WHAT IS PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD] or peripheral arterial disease (PAD] is the blockage of arteries of the lower limbs due to accumulation of cholesterol, calcium and plaques. This leads to reduced blood and oxygen supply to the legs and may eventually lead to limb amputations as well as suffering due to rest pain and gangrene.
WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS OF PAD?

When to see a doctor
If you have leg pain, numbness or other symptoms, don’t dismiss them as a normal part of aging. Call your doctor and make an appointment.
- Over age 70
- Over age 50 and have a history of diabetes or smoking
- Under age 50, but have diabetes and other peripheral artery disease risk factors, such as obesity or high blood pressure.
Peripheral artery disease is often caused by atherosclerosis. In atherosclerosis, fatty deposits (plaques) build up in your artery walls and reduce blood flow.
Although the heart is usually the focus of discussion of atherosclerosis, this disease can and usually does affect arteries throughout your body. When it occurs in the arteries supplying blood to your limbs, it causes peripheral artery disease.
Less commonly, the cause of peripheral artery disease may be blood vessel inflammation, injury to your limbs, unusual anatomy of your ligaments or muscles, or radiation exposure.
What are the treatment options for PAD?
Medicines: Not all patients require major surgery if diagnosed in time. Certain medicines are useful along with control of risk
factors like smoking, diabetes, hypertension and high cholesterol.
Walking exercises: Useful for improving claudication and thus walking distance. But this may not be suitable for patients who have ulcer or gangrene.
Angioplasty and Stenting: Minimally invasive techniques through need ie punctures and utilizing endovascular balloons or stents have revolutionized the treatment of PAD. There have been substantial developments in the skills and resources utilized for endovascular procedures over the past decade. Continuously upgrading expertise has led to the development of drug coated balloons, hysterectomy devices and vascular mimetic stents, which promise to deliver better results than previous devices.
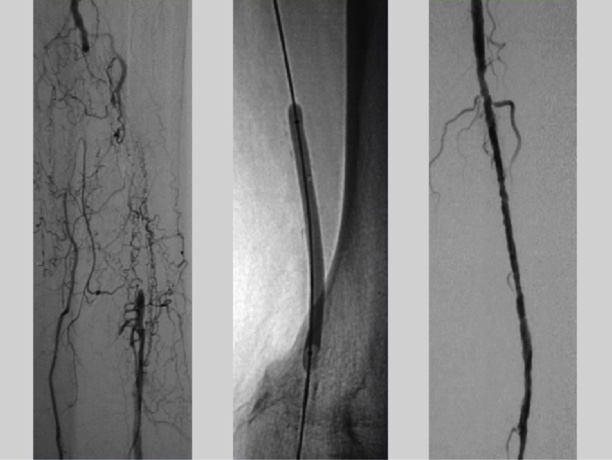
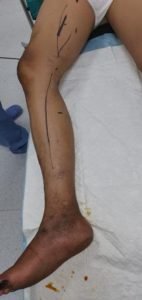
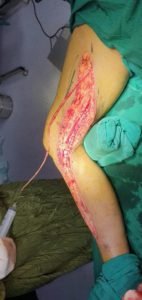
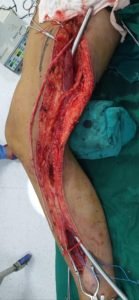
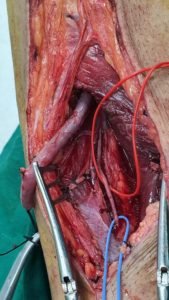
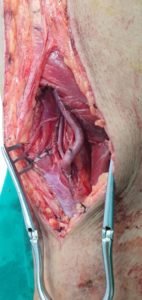
Bypass surgery
Your doctor may create a graft bypass using a vessel from another part of your body or a blood vessel made of synthetic fabric. This technique allows blood to flow around — or bypass — the blocked or narrowed artery.
Thrombolytic therapy
If you have a blood clot blocking an artery, your doctor may inject a clot-dissolving drug into your artery at the point of the clot to break it up.